

Chaudhary, A., Belani, M., Maheshwari, N., Parnami, A.
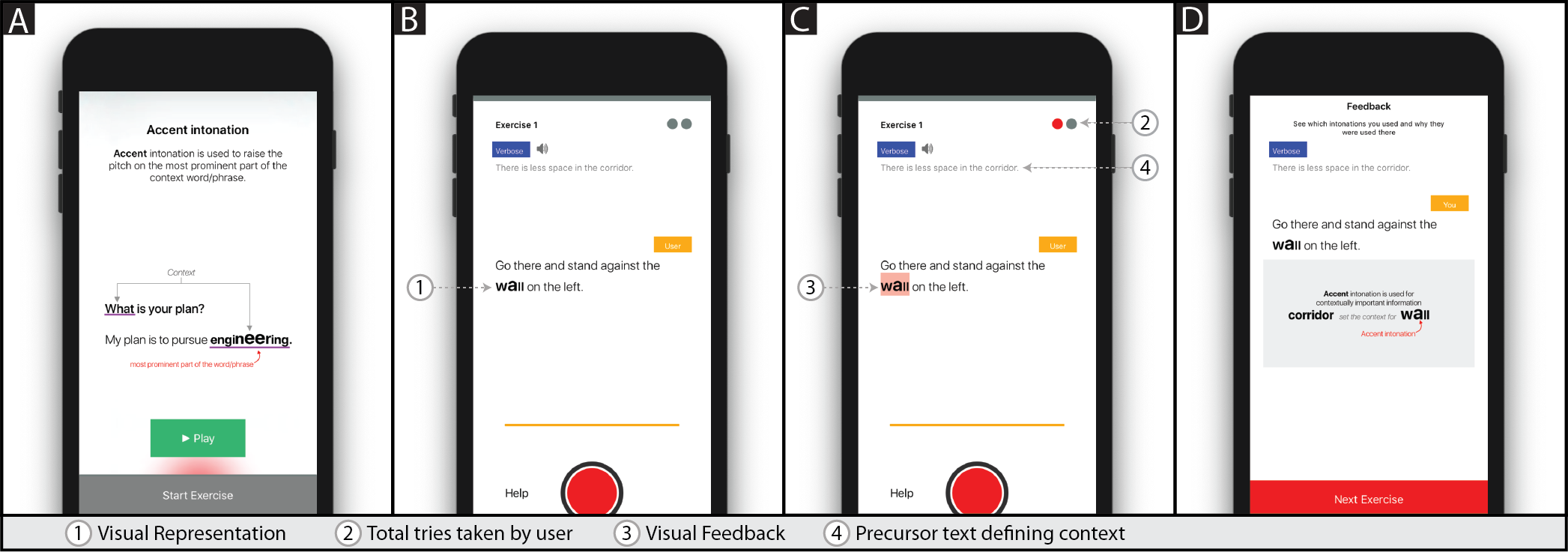
ESL (English as a second language) speakers tend to follow the tone structure of their first language, making their speech difficult to understand for native speakers, thereby limiting their opportunities for education and employment. To address this problem, we build an interactive smartphone-based educational mobile application using the user-centered design process. This application teaches English intonations based on globally consistent pitch patterns through conversations with a trained chat assistant, which inculcates expert linguists' teaching principles. After co-designing the application's parameters with primary stakeholders and expert visual designers, we assess its effectiveness by measuring the pre and post-performance of the users after the system usage, using various quantitative measures, like intonation scores, SEQ, and SUS. Feedback from users suggests that ESL speakers find significant improvement in the perception of their vocal expressions, thereby highlighting the necessity of such a system in improving the quality of conversations that people have in general.
To appear in MobileHCI’21